Research topics
The main research topics of DAMA-UPC are oriented to performance, exploration and quality in data management, focusing particularly on large data volumes. We investigate the creation of new data structures, algorithms, methods and applications in the area of Data Management that make it easier to manipulate large amounts of data.
Smart Mobility
Integrating data from various sources such as mobile apps, sensors, government data, private data and Open Data is playing a key role if we want to develop better understanding on how citizens behave and how cities evolve. Applying this knowledge is going to become a crucial for the next generation of Smart Cities. Graph databases allow the visualisation and analysis of all the data generated in a modern city, making it actionable through associated Mobile Apps.
Graph Databases
Manage huge data networks!
The size of the volume of data manipulated in any organization is always increasing. The analysis of these has an increasingly greater role In the decision-making of large enterprises or in the study of various fields, Academics and non-academics, which have an impact on the improvement of life Society in which we live.
Current Projects
- Graph Benchmarking
- Graph data transactions
- Graph query algebra
- Distributed Graph Databases
Social Networks and Graph Analysis
Graphs are everywhere!

Twitter, Facebook and the whole Internet is providing billions of related data items, which form huge networks of relationships. Visual inspection of such datasets to derive information from these datasets is not feasible, and it is necessary to design algorithms that perform graph mining. We are working on graph data analysis algorithms for such networks that are scalable and can process huge graphs.
Current Projects
- SCD: Scalable Community Detection. (Link to GitHub code)
- Query suggestion using knowledge bases
Past Topics
Relational Database Management Systems
The use of Relational Database Management Systems as powerful tools to store, modify and access data in a database is completely generalized world-wide. The complexity of RDBMSs range from the most simple applications, designed for home use or small companies with modest information storage requirements, like Microsoft Access, to very complex and sophisticated RDBMSs, such as DB2 UDB, Oracle or Microsoft SQL Server, used in critical situations where the huge amount of data to be manipulated requires advanced techniques to improve performance.
However, the rapid and continuous growth of the amount of data to be stored and manipulated in-creases beyond the possibilities of current hardware and software, jeopardizing the acceptable performance of RDBMSs.
Distributed Search Engines and Question Answering
Cooperative Caching and cache aware load balancing
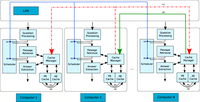
The details of the architecture in major search engines have evolved with the new technology and algorithms available, however some fundamental characteristics are latent in their designs: distributed computing and data caching. One single computer is far from achieving the throughput required by major search engines, and the engineers deploy these systems on clusters of computers, often based on commodity hardware. Although this architecture accumulates the processing power of several computing nodes, it is not enough to rely on the accumulation of hardware because the amount of resources needed would become prohibitive. This project targets the improvement of cache-aware techniques for distributed systems in order to improve the system performance.
- Cooperative caching for question answering
- Search Environments for Media (Semedia, EU-FP6 project)
Performance Aspects of Data Privacy and Anonymization for Very Large Datasets
When size matters!
- Genetic Algorithms for Multivariate Microaggregation
- Improving Performance Aspects of Anonymization Methods
Share: